Single site porphyrine-like structures advantages over metals for selective electrochemical CO2 reduction
Alexander Bagger, Wen Ju, Ana Sofia Varela, Peter Strasser and Jan Rossmeisl
A. Bagger et al. / Catalysis Today 288 (2017) 74–78DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2017.02.028Description
In this paper we address our goal of achieving higher selectivity towards CO2RR. We discuss the reaction mechanisms for both HER and CO2RR on metals and porphyrine-like structures. The single metal site in a porphyrine-like structure requires an ontop site binding of hydrogen, compared to the hollow site binding of hydrogen on a metal catalyst surface. The difference in binding site structure gives a fundamental energy-shift in the scaling relation of ∼0.3 eV between the COOH* vs. H* intermediate (CO 2 RR vs. HER)
The Database
Download metal databaseDownload porphyrine-like databaseDownload molecule databaseKey-value pairs: Description
Given and used in python scripts, but also listed below here.
Key words for metals database:
Metal: 'Rh','Pd','Ir','Pt','Au','Ni','Cu','Co','Ag','Fe','Ru'
ads: 'COOH', 'H','CO', 'Clean'
position: 'Hollow', 'Ontop', ''
Key words for porphyrine-like database:
Metal: 'Cu','Ni','Pd','Pt','Co','Rh','Ir','Fe','Ru','Mn'
ads: 'COOH', 'H','CO', 'Clean'
Key words for molecule database:
Molecule: 'CO2', 'CO', 'H2'
COOH* vs. H* scaling for metal and porphyrine structures
The script plots the COOH* energy as a function of the H* energy for both metals and porphyrine like structures.
Download script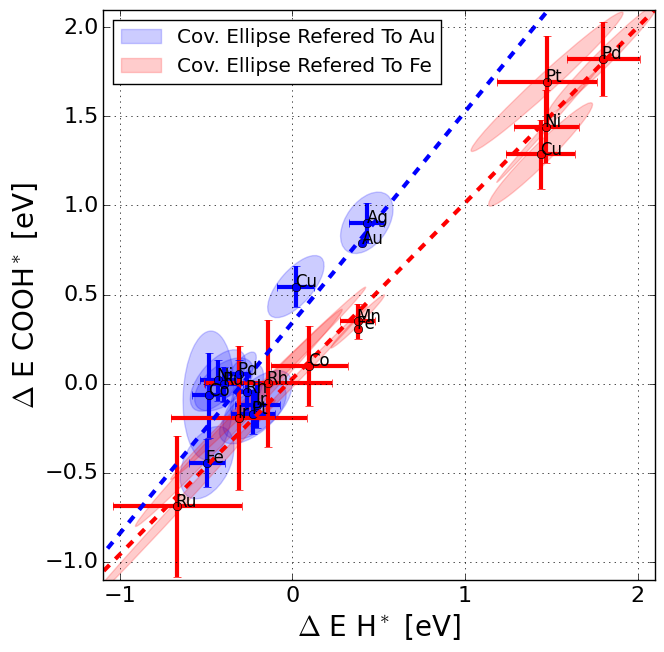
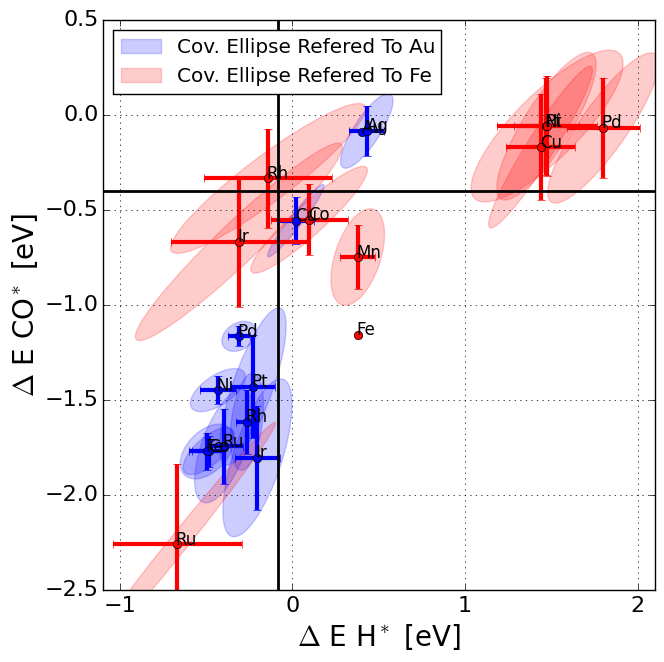
CO* vs. H* scaling for metal and porphyrine structures
The script plots the CO* energy as a function of the H* binding energy on metals and porphyrine-like structures.
Download script