KatlaDB - Theoretical Catalysis Database
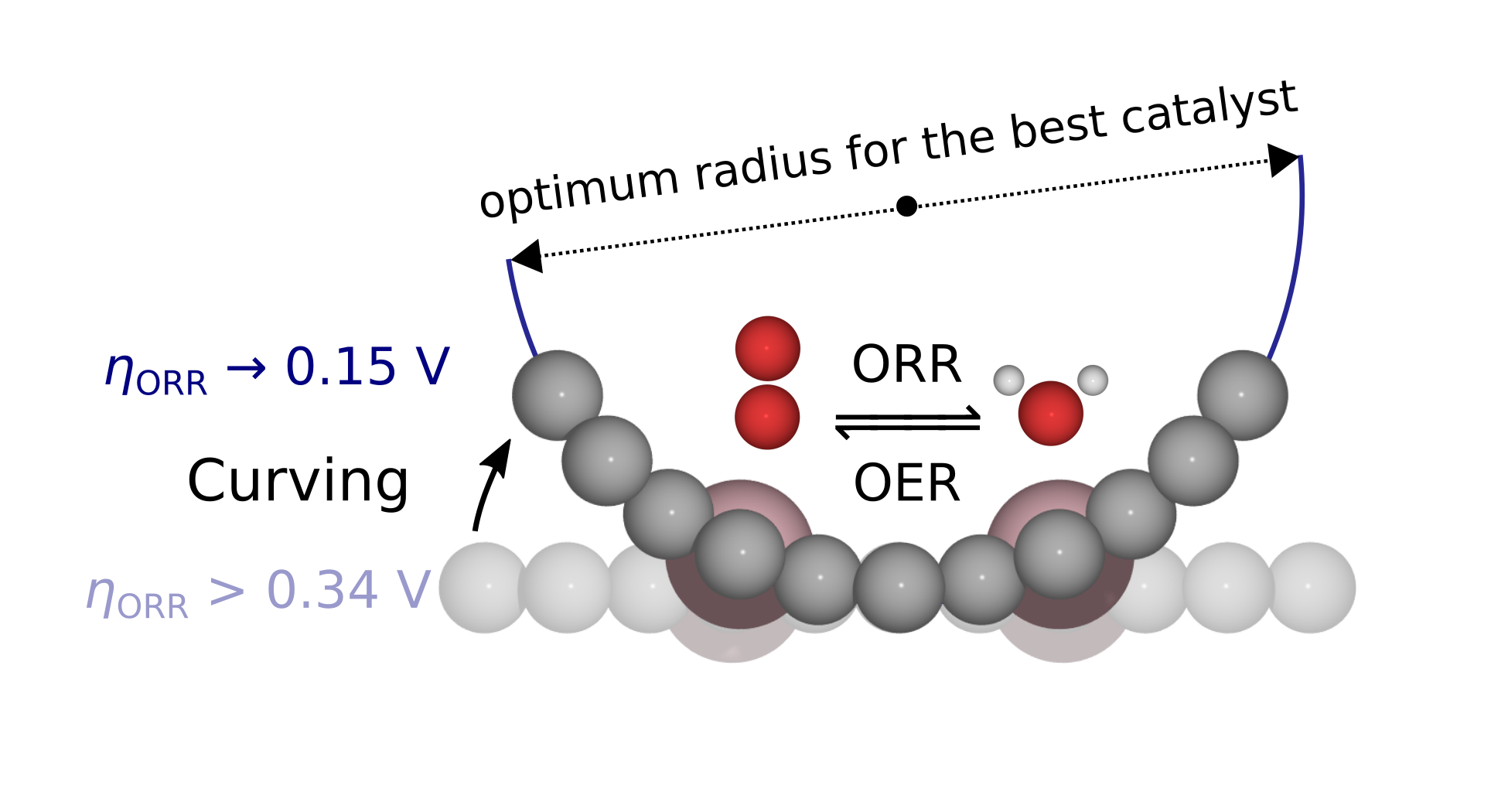 |
Surface curvature effect on dual-atom site oxygen electrocatalysis We show the effect of surface curving on the OER/ORR intermediates' energies and energy differences, overpotentials and OOH dissociation barrier. |
 |
|
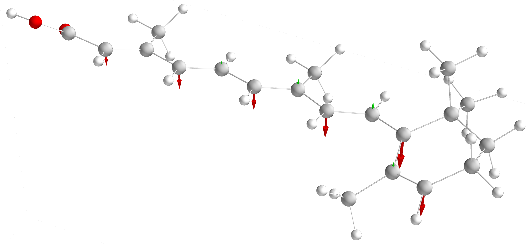 |
We investigate the exchange interaction of deprotonated retinoic acid molecules across hydrogen bonds.
|
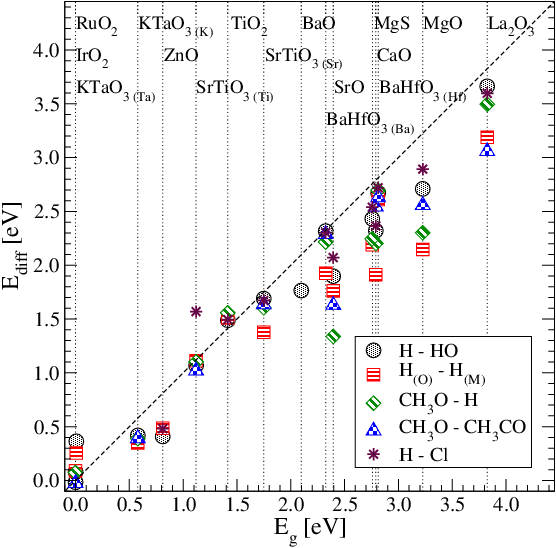 |
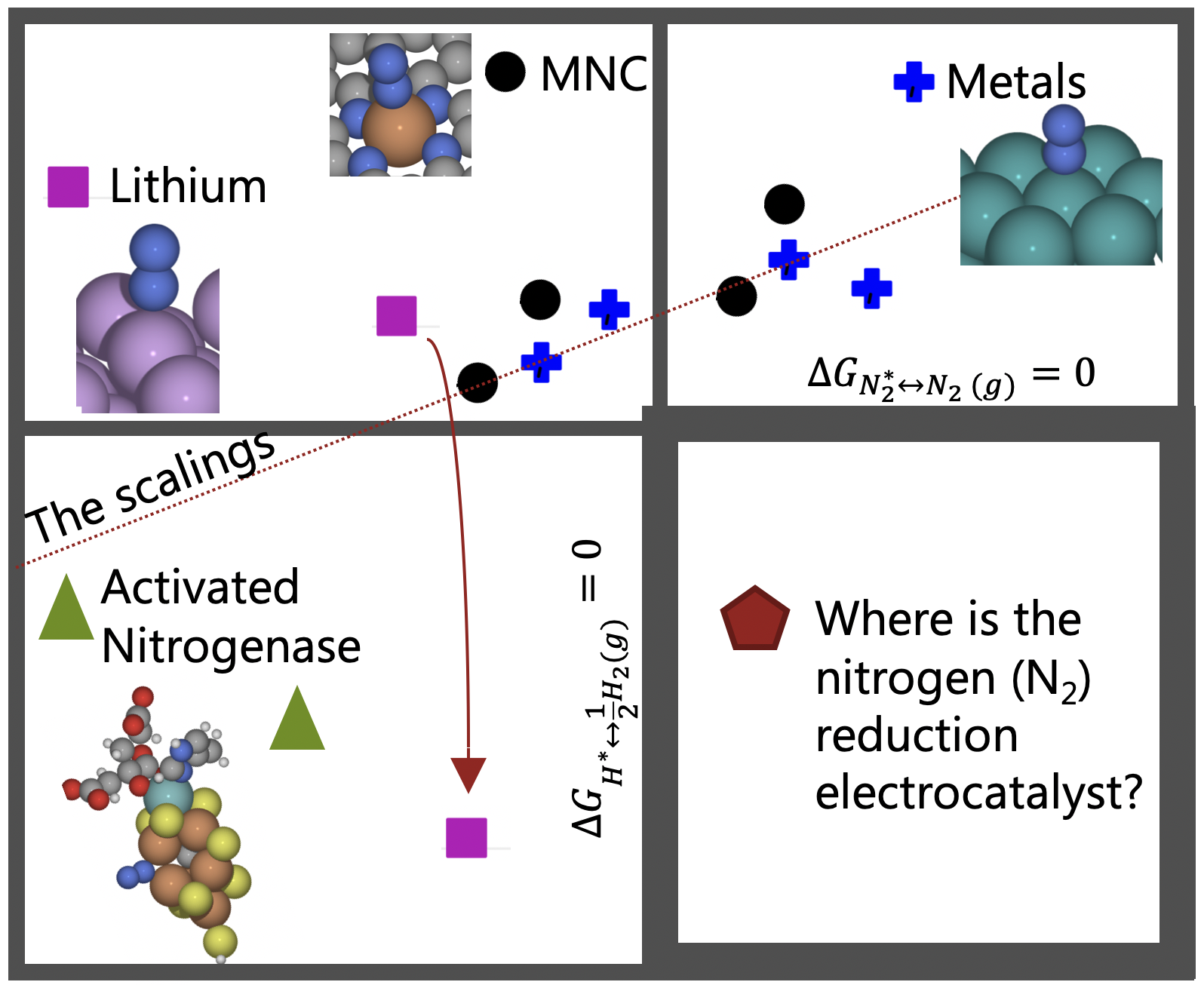
We investigate the interaction energy of coadsorbed fragments on band gap oxides and we propose to use the band gap as a descriptor of the interaction energy.
|
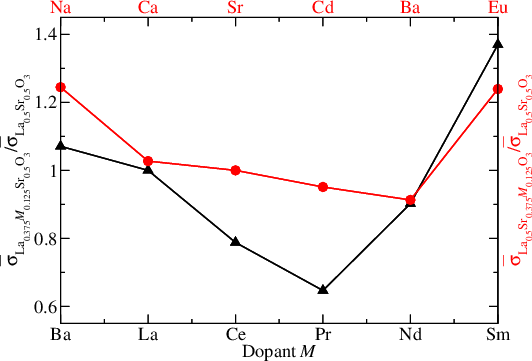 |
We have calculated the electrical conductivity of the SOFC cathode contact material La1−xSrxCoO3−δ at 900 K. Furthermore, we have studied the chemistry of neutral and charged intrinsic and extrinsic defects (dopants) in La0.5Sr0.5CoO3 and calculated the conductivity of the doped systems. In particular, we find that doping with Sm on the La site should enhance the conductivity.
|
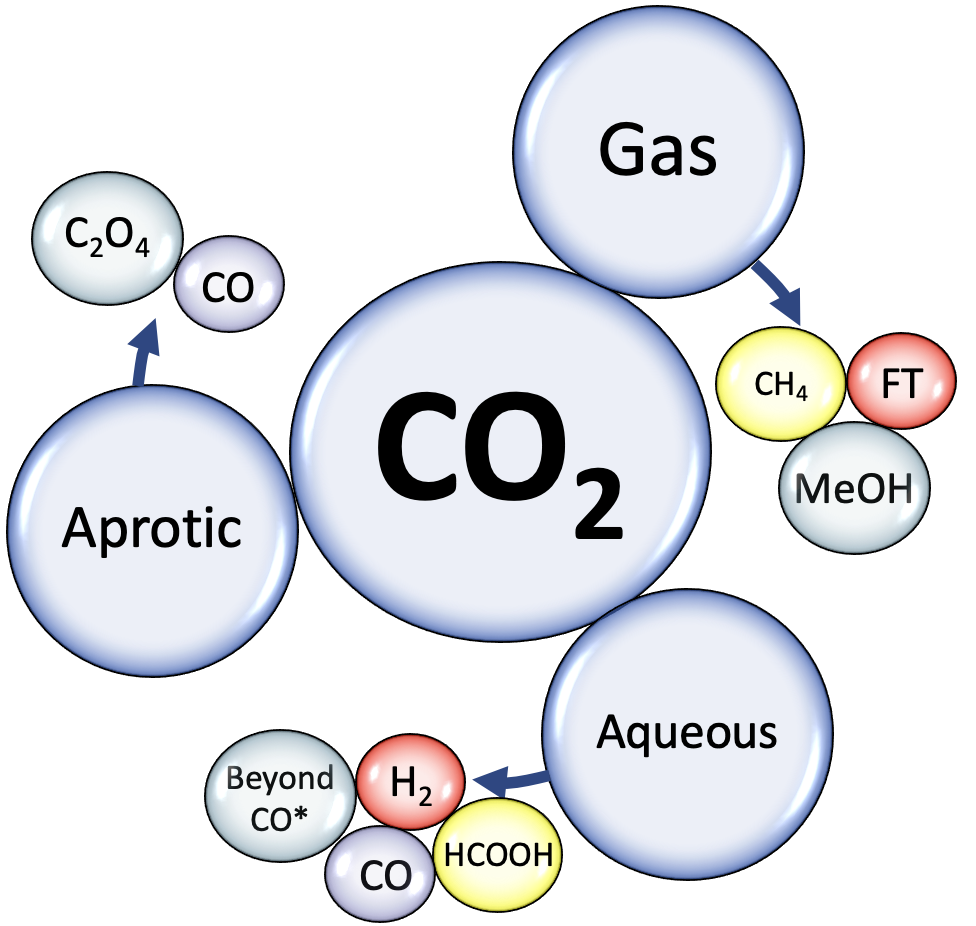 |
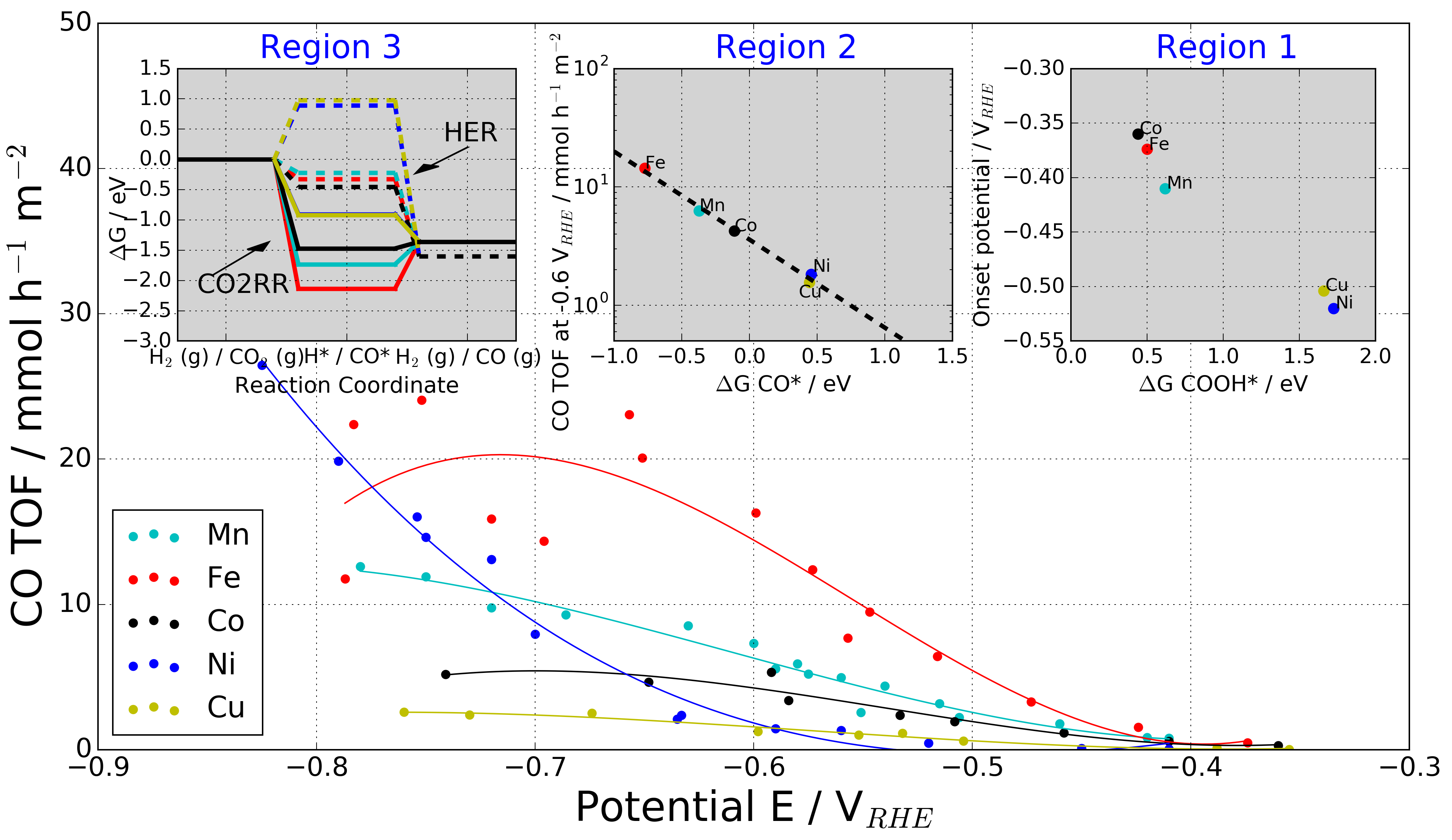
We created a simplistic view on CO₂/CO reduction reaction in the three phases. We used the reaction binding as important reaction descriptors, which match to the catalyst product. We show that (i) for the gas phase reaction the binding of *CO vs *O give a good description, (ii) for the aqueous phase binding of *CO vs *H give a good description, and (iii) for the aprotic phase we show by the *CO vs *H that the reaction is not determined only by the binding energies.
|
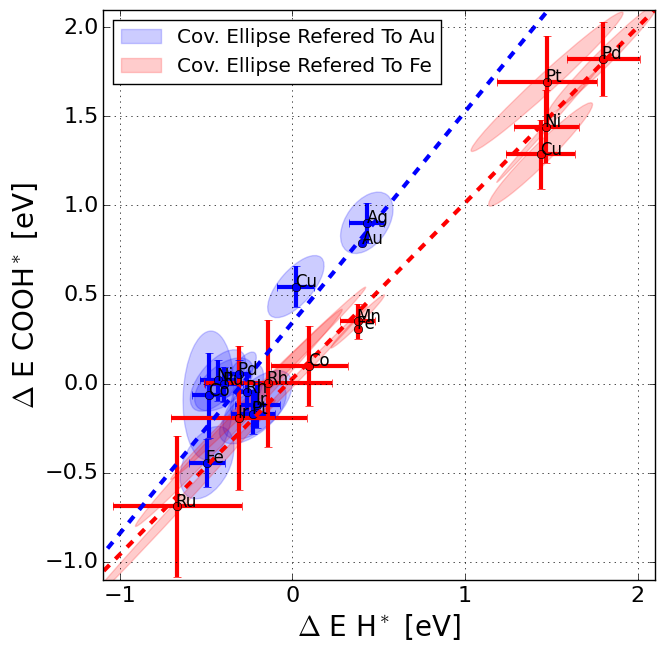 |
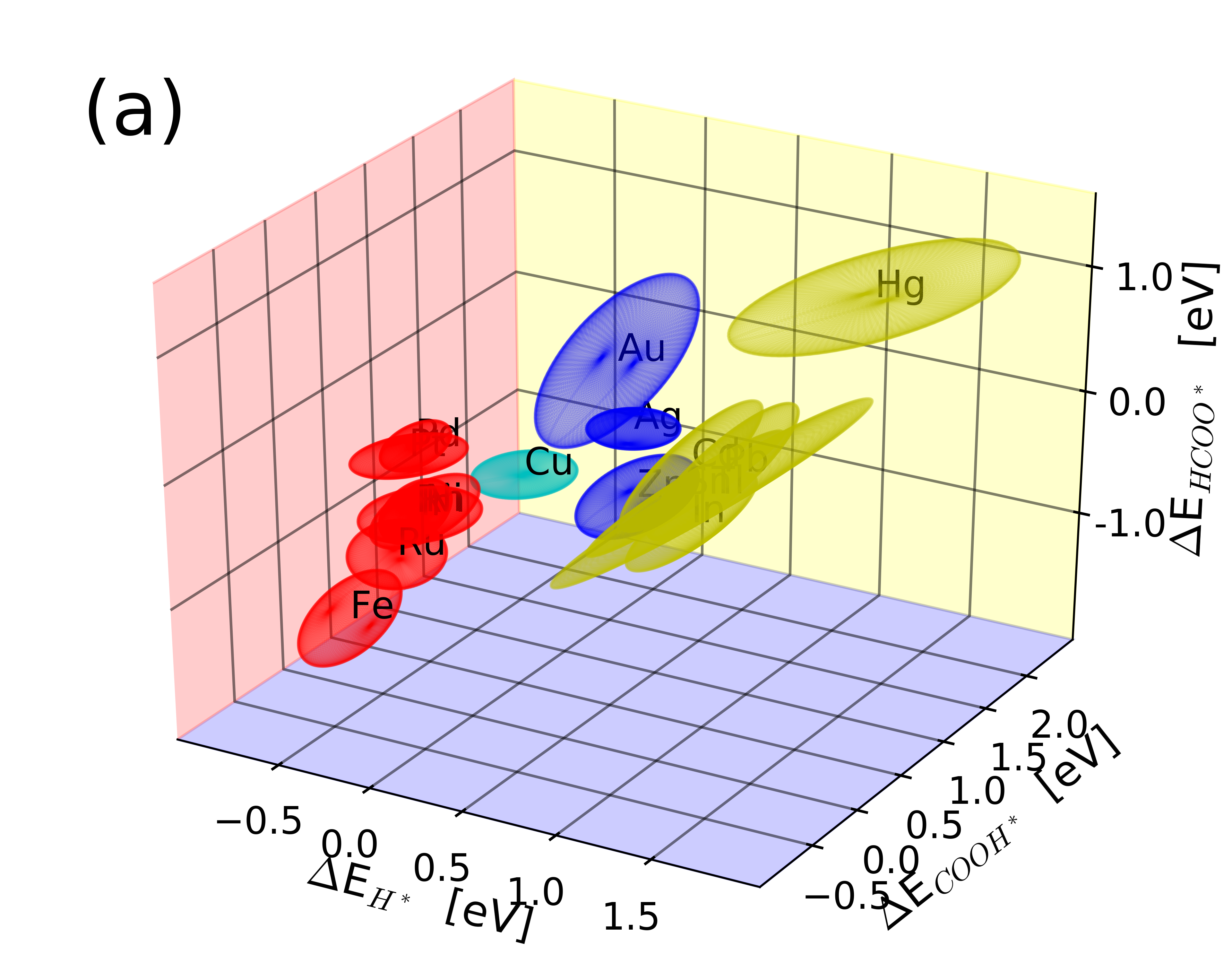
The data is supplementary material for the paper, which includes all structures and binding energies calculated. Further, figures have been plotted with labels for all metals and porphyrine-like structures.
|
|
|
Dimethyl carbonate is an environmentally friendly precursor in various chemical reactions and is currently synthesized by hazardous processes. An electrocatalytic approach could result in a process abiding to the principles of Green Chemistry. Herein we demonstrate how density functional theory (DFT) calculations and experiment advance our understanding of electrocatalytic production of chemicals. Using density functional theory, we form design criteria for dimethyl carbonate electrosynthesis on metallic surfaces. The criteria are based on adsorption free energies of reactants and reaction energies of possible products. The design criteria allow us to identify copper as an interesting candidate for the electrode material as it is classified as being selective to dimethyl carbonate and requires ≈ 1 V lower potential than a gold electrode. By further addressing electrode stability copper was found to dissolve and produce copper-carbonyl species which lead to dimethyl carbonate as a consequence of a reaction in the solution, therefore not occurring by surface electrocatalysis. This shows that the design criteria presented herein are necessary but not sufficient requirements that the ideal electrode should satisfy.
|
|
|
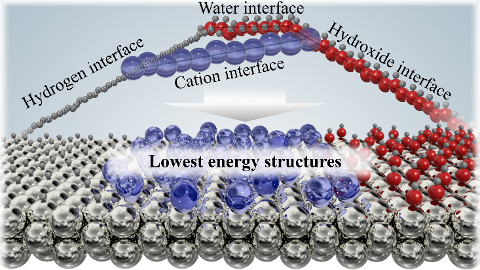
We present atomic-scale structures of the Pt(111)/water interface, by calculating distributions of atomic distances as functions of pH. The structure of the Pt(111)/water interface is a particularly interesting model system in electro-catalysis for proton exchange reactions, especially the oxygen reduction reaction in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Further insight into such reactions requires accurate simulations of the electrolyte structure in the interface. The study displays many interesting details in the behaviour of the electrolyte structure, e.g. that the electrolyte structure average responds to the presence of protons by a H-down water orientation and that hexagonal adsorbed water layers are present only when they are anchored at the surface by HO*. New adsorbate configurations were also found at 5/12 ML coverage of HO*, suggesting an explanation for reported cyclic voltammetry experiments. The present study is a step towards a more complete understanding of the structure of the electrochemical interface on the atomic scale.
|
 |
The data is supplementary material for the paper, which includes all structures, binding energies and energy ensembles. Further, plotting script is given to plot Figure 1 of the paper and the layout can be used to also achieve and plots other data from the database.
|
 |
The data is supplementary material for the paper, which includes all structures and binding energies calculated. Further, experimental data together with plotting script for Figure 5 in the paper can be downloaded.
|
|
Enhanced Carbon Dioxide Electroreduction to Carbon Monoxide over
Defect-Rich Plasma-Activated Silver Catalysts The data is supplementary material for the paper, which includes all structures and binding energies calculated.
|
|
|
Accessing the Inaccessible: Analyzing the Oxygen Reduction Reaction in the Diffusion Limit A numerical site-blocking model to simulate ORR currents in the absence of mass transport limitations. |
|
|
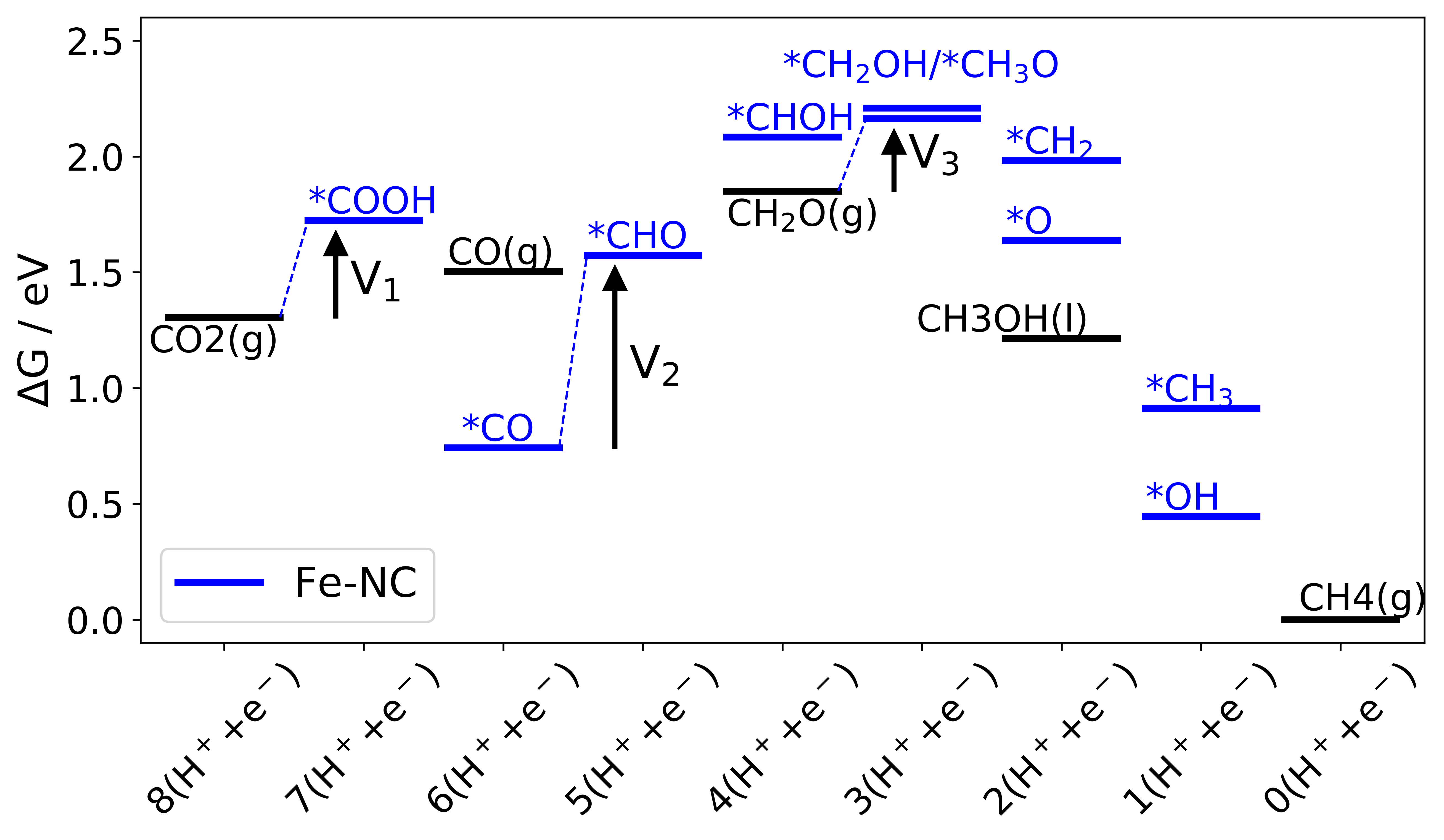
Fundamental limitation of electrocatalytic methane conversion to methanol A database with all structures and scripts for plotting figures. |
|
|
Oxidation of Ethylene Carbonate on Li Metal Oxide Surfaces
Contains a database file with structures and energies, and scrips for plotting all figures from the paper. |
|
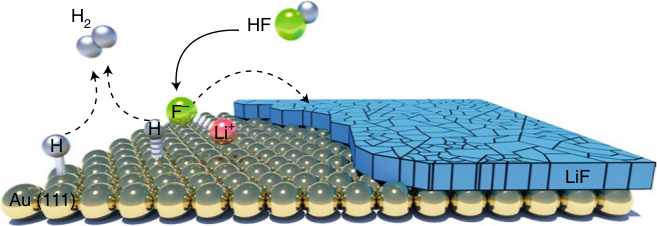 |
Electrocatalytic transformation of HF impurity to H2 and LiF in lithium-ion batteries
We have discussed the formation of H2 and LiF from a dissociation of HF in Li-ion batteries. The database contains all the calculations used in the paper to produce the phase diagram of Li and identify trends. |
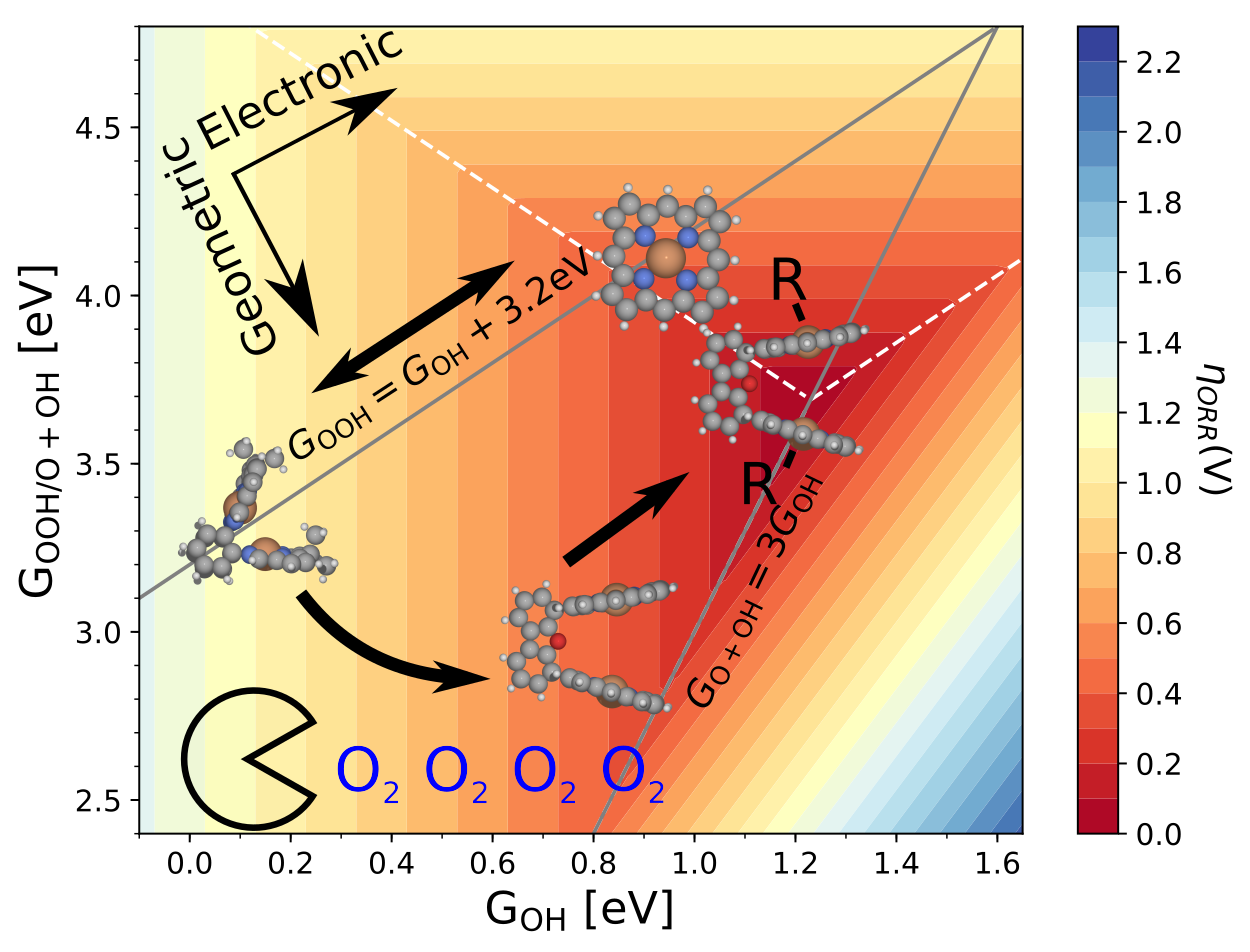 |
Climbing the 3D Volcano for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction Using Porphyrin Motifs
Contains a database file with structures and energies, and scrips for plotting all figures from the paper. |
 |
Electrochemical CO reduction: A property of the electrochemical interface
Contains a .zip file with multiple folders with databases and scrips for plotting figures from the paper. |
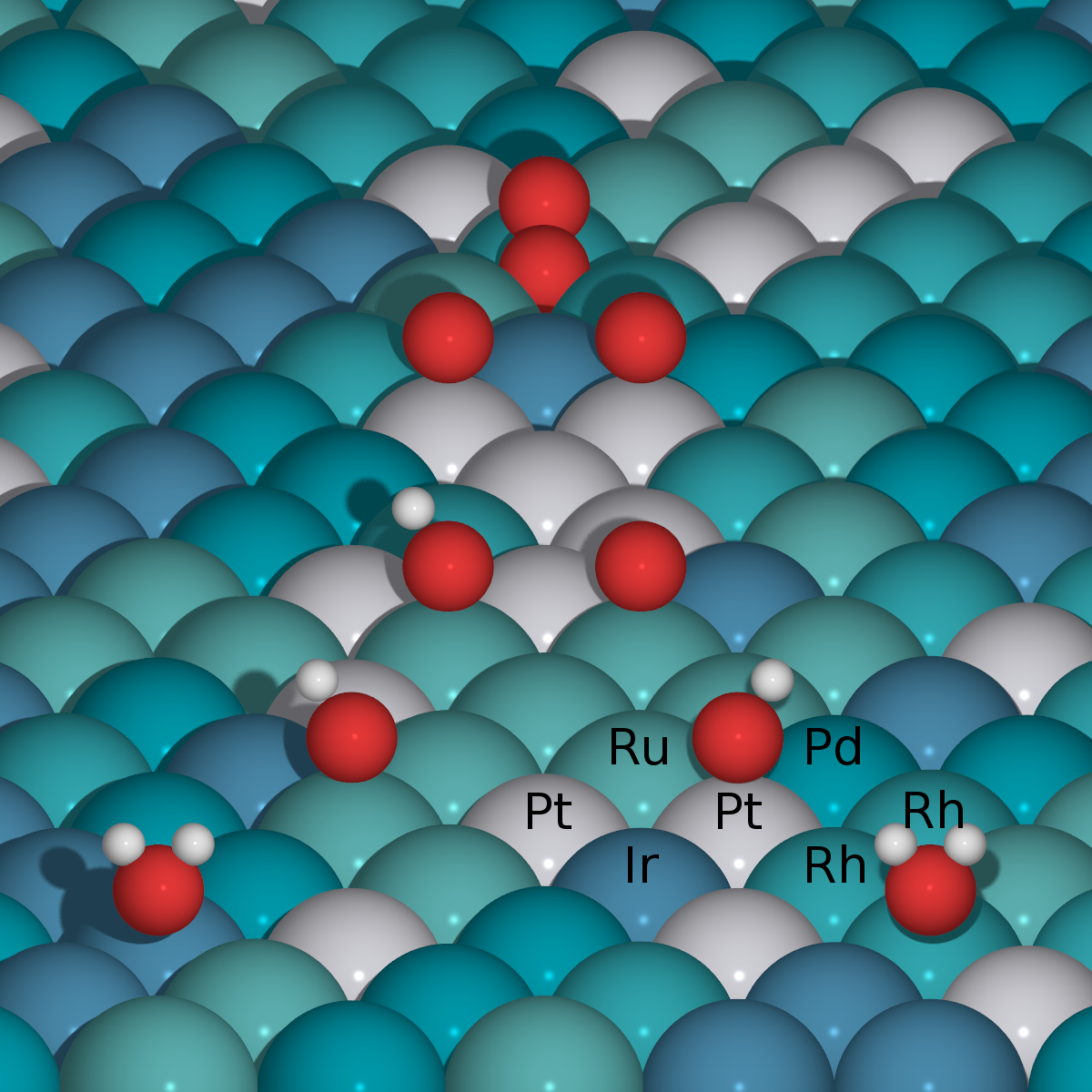 |
High-Entropy Alloys as a Discovery Platform for Electrocatalysis |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Realistic Cyclic Voltammograms from Ab Initio Simulations in Alkaline and Acidic Electrolytes Contains a .zip file with databases and scripts for plotting the figures from the paper. |
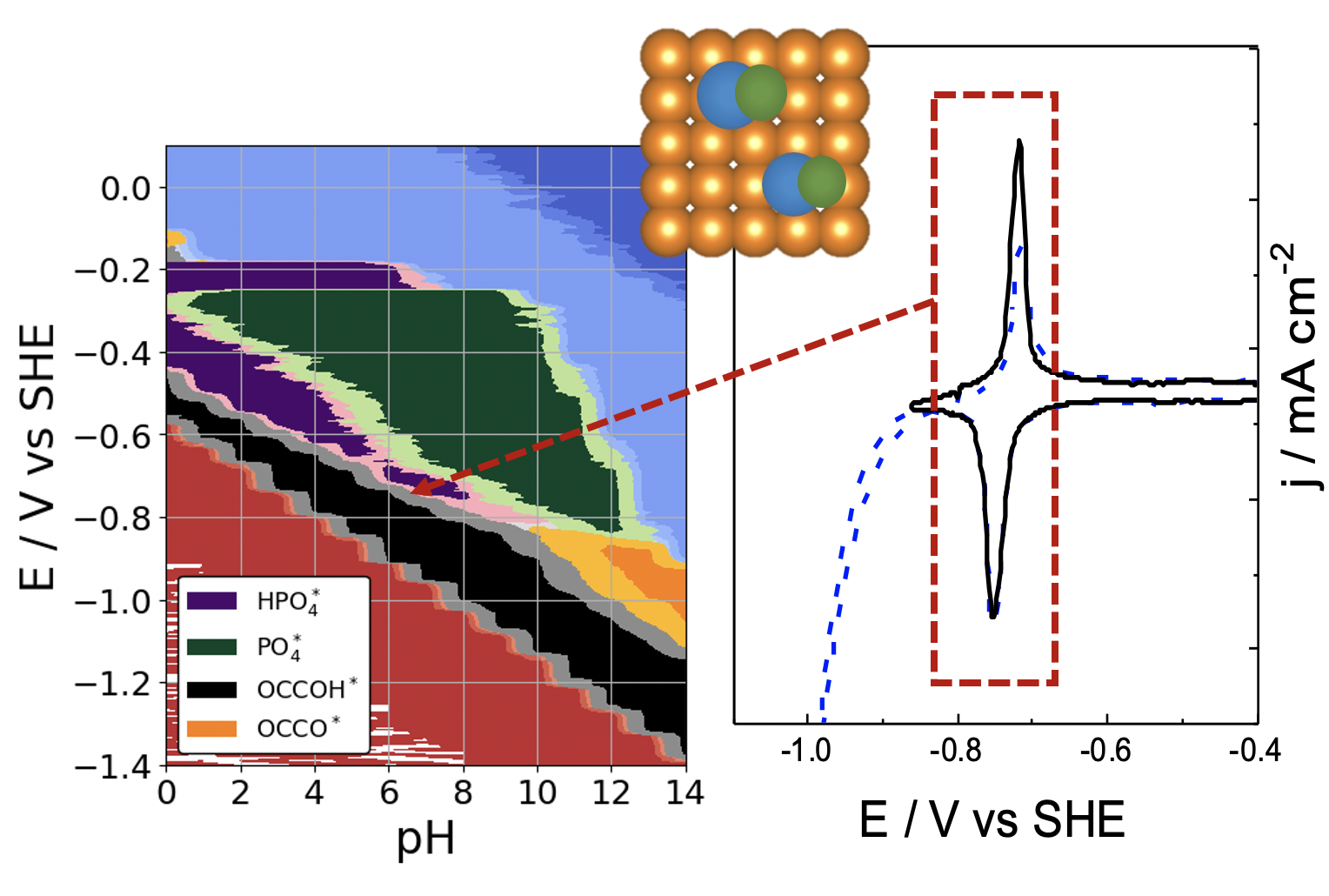 |
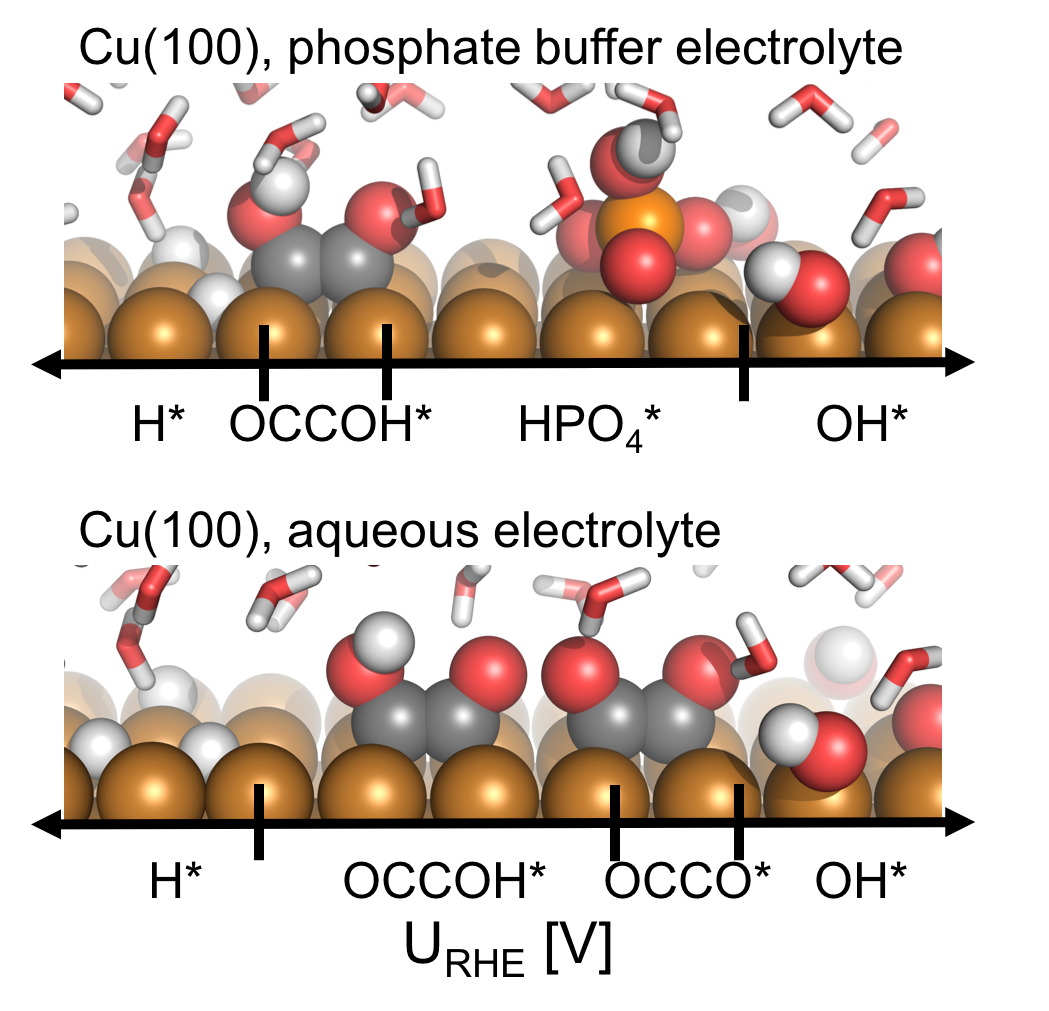
pH and anion effects on Cu-phosphate interfaces for CO electroreduction Contains a .zip file with databases and scripts for plotting figures from the paper. |
 |
|
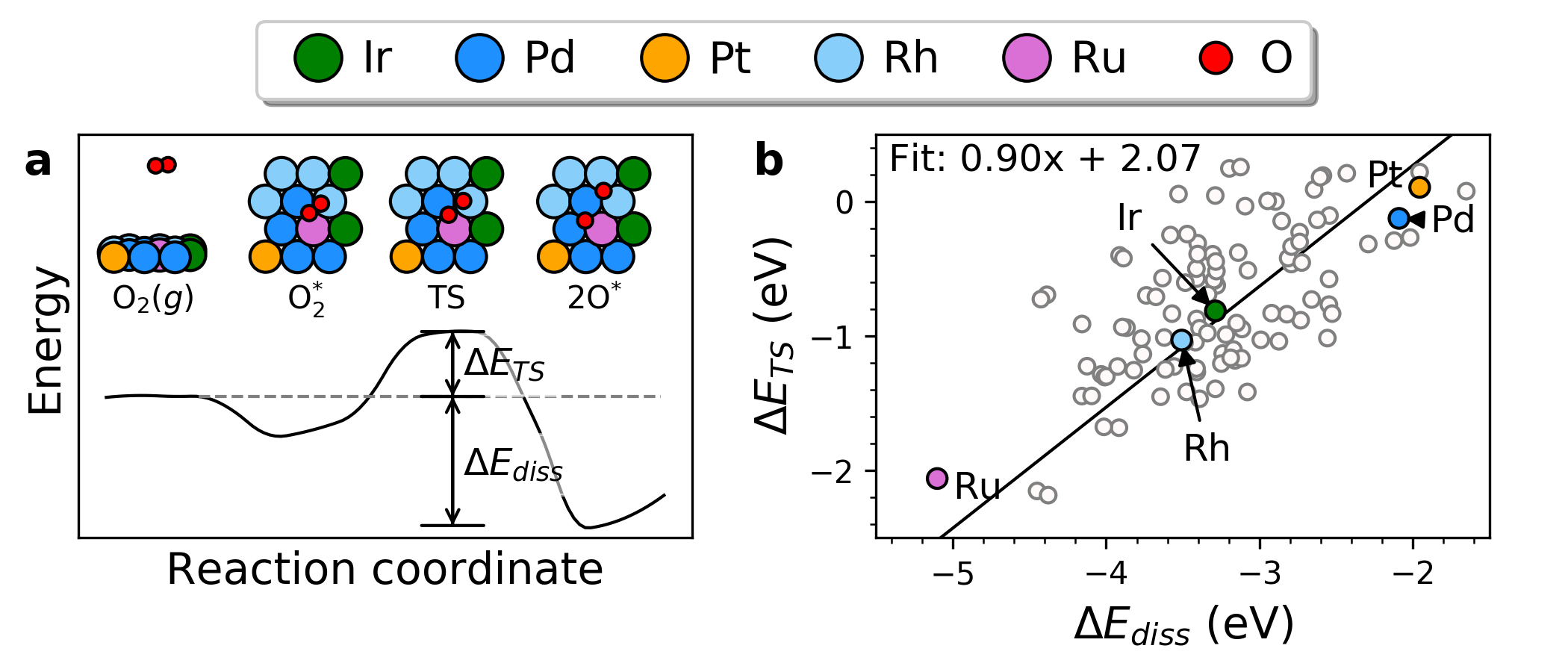
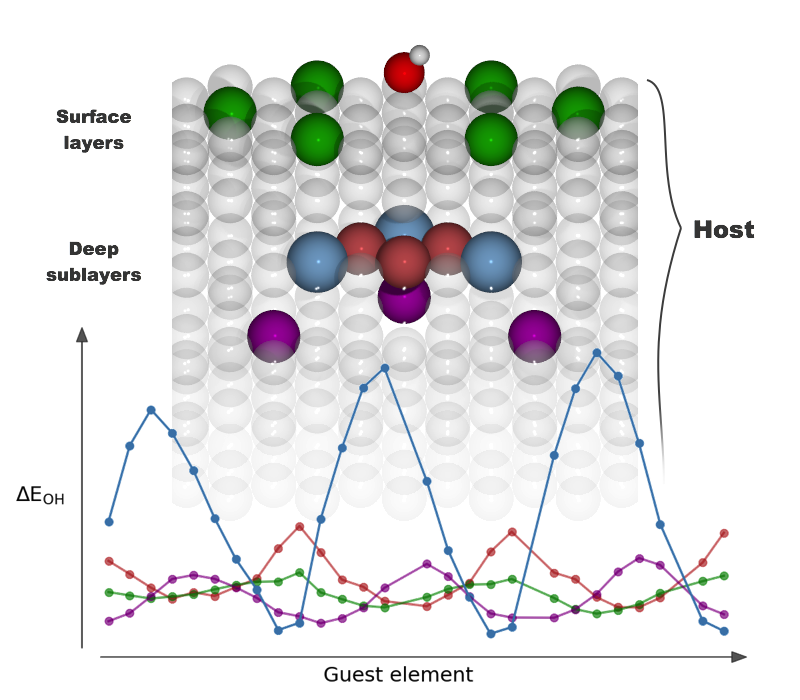 |
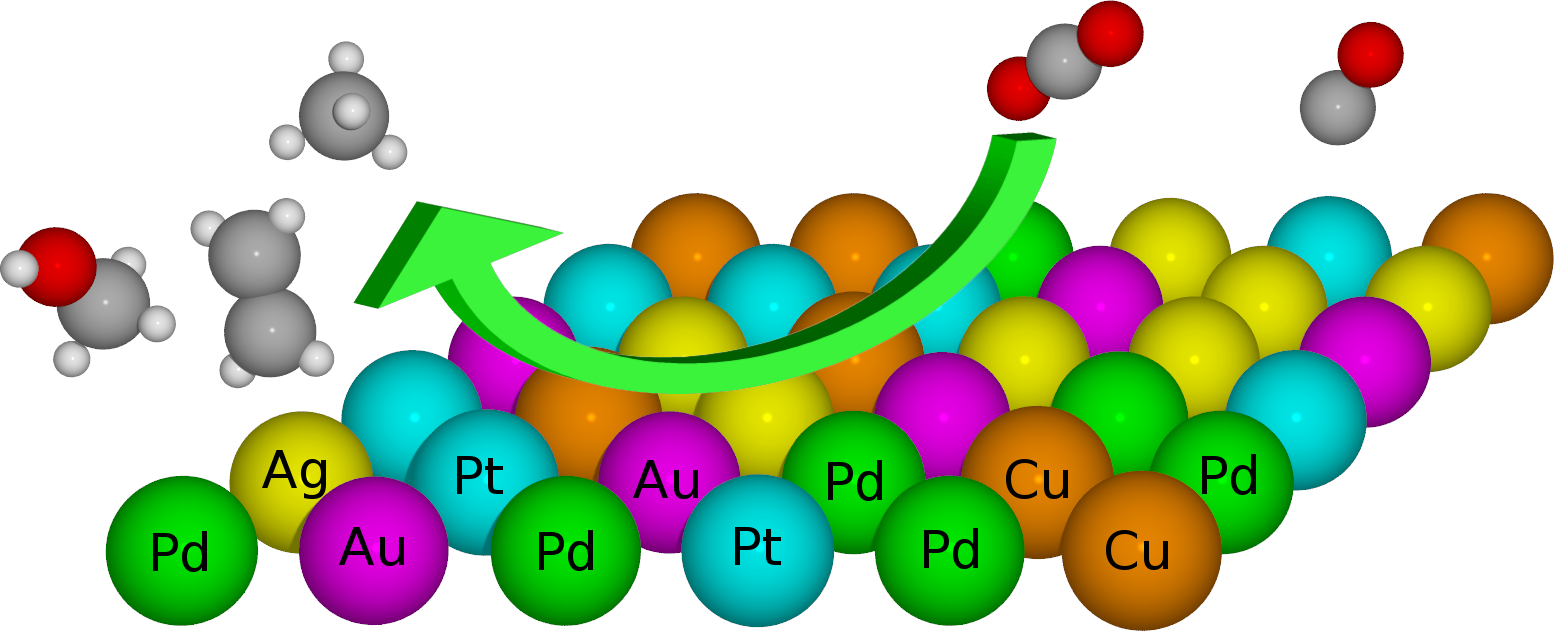
Long‐Range, Directional Ligand Effects in Metallic Alloys A statistical analysis uncovers what atomic positions, near the binding site on the surface of an alloy, exert an electronic effect on the adsorbate–surface bond. |
 |
Capturing the Formation Mechanism of Additive-Mediated Intermetallic PdCu Nanoparticles Files for reproducing the DFT calculations on the stability of the investigated phases of PdCu. |
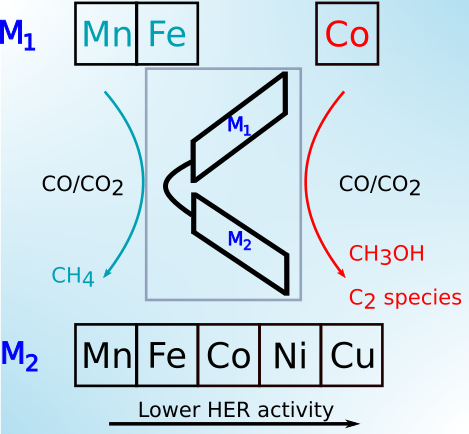 |
Three-Dimensional Carbon Electrocatalysts for CO2 or CO Reduction Contains a database file with structures and energies, and scrips for plotting all figures from the paper. |
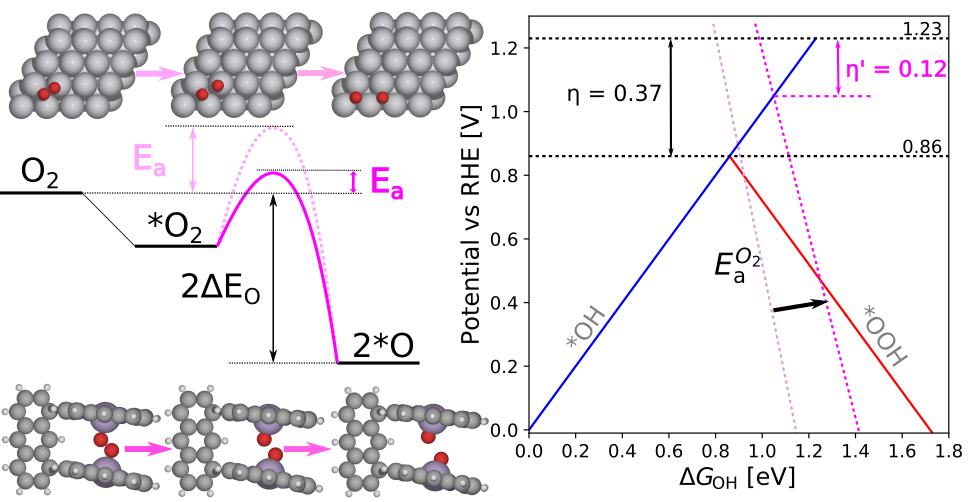 |
Insights in the Oxygen Reduction Reaction: From Metallic Electrocatalysts to Diporphyrins Contains a zip file with structures and energies, and scrips for plotting figures from the paper. |
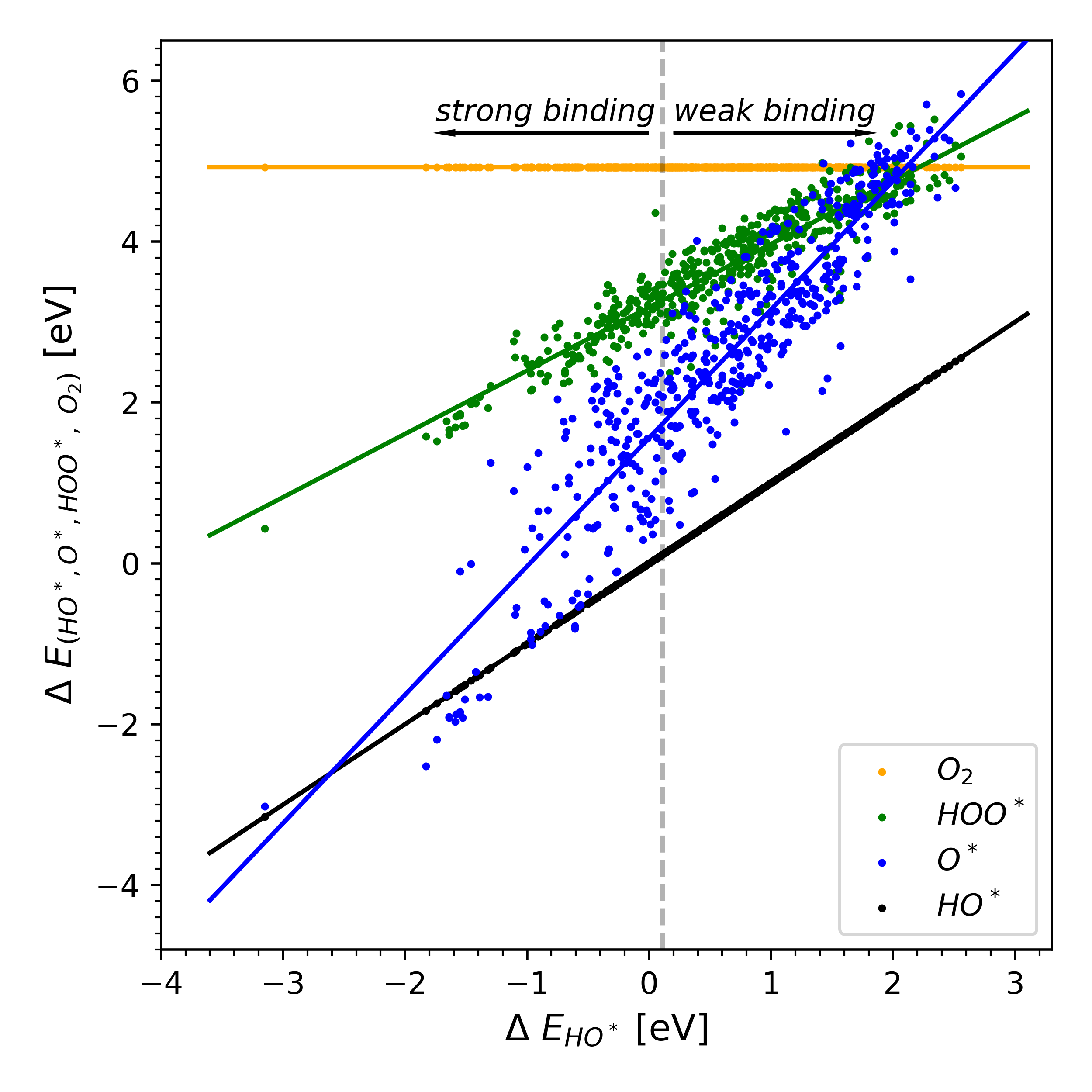 |
Oxygen evolution reaction: a perspective on a decade of atomic scale simulations |
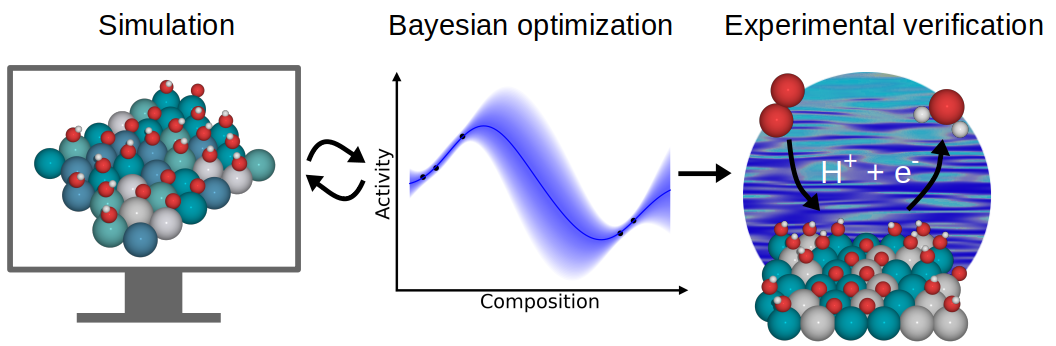 |
Bayesian Optimization of High-Entropy Alloy Compositions for Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction |
 |
|
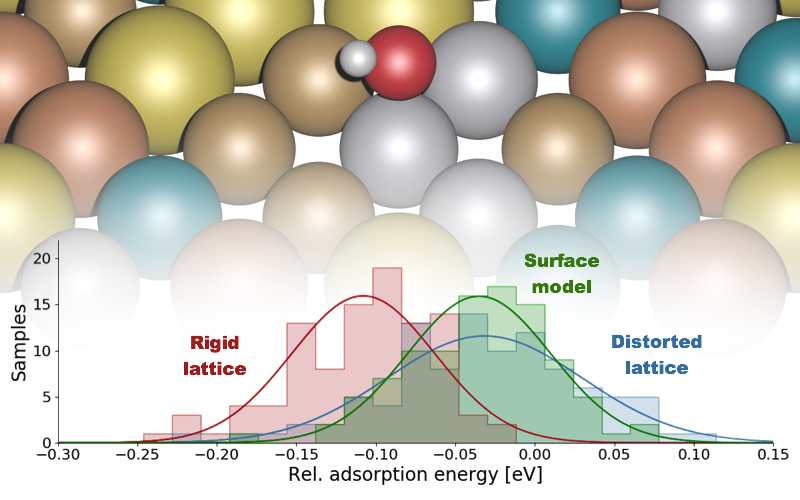 |
Lattice distortion releasing local surface strain on high-entropy alloys |
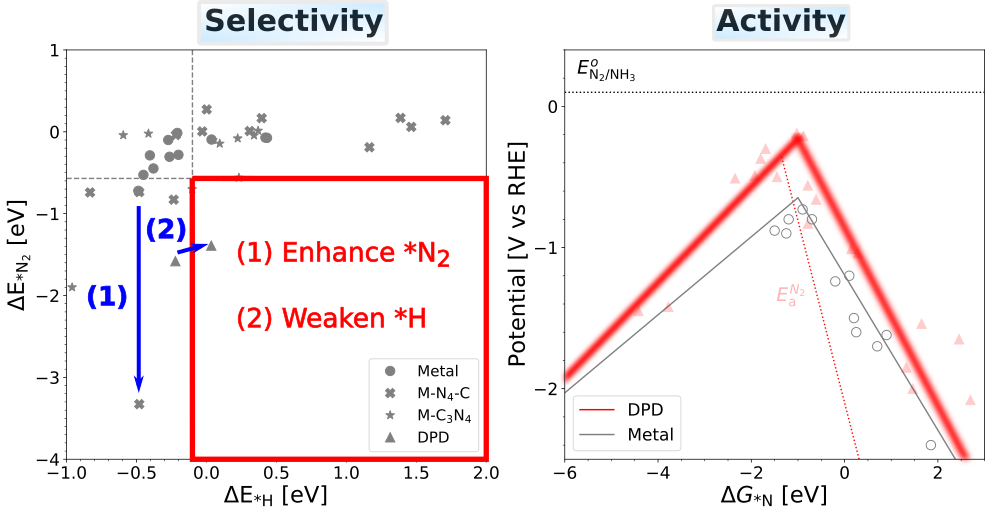 |
Improved Electrocatalytic Selectivity and Activity for Ammonia Synthesis on Diporphyrin Catalysts |
| Ab initio to activity: Machine learning assisted optimization of high-entropy alloy catalytic activity | |
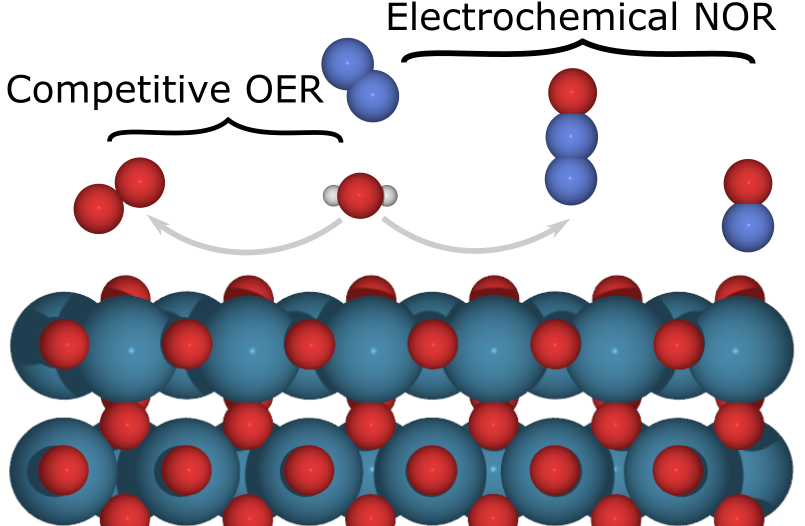 |
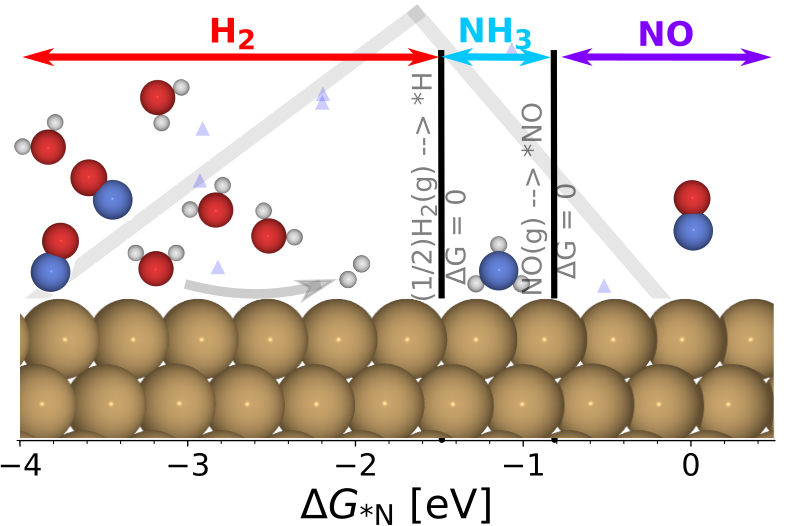
Limitations of Electrochemical Nitrogen Oxidation toward Nitrate |
| Electrochemical Synthesis of Urea: Co-reduction of Nitric Oxide and Carbon Monoxide |

